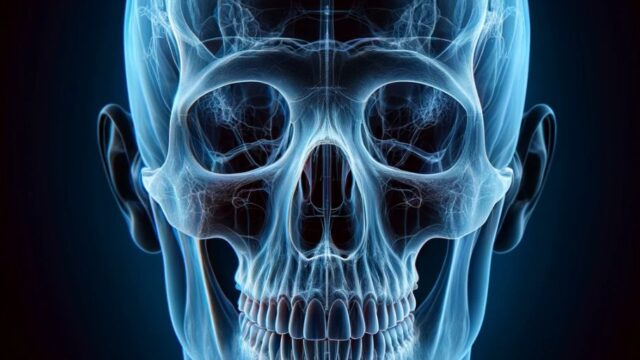
Japanese ver.
Radiopaedia (AP view)
Radiopaedia (PA view)
Purpose
Observation of skull fractures, dislocations, tumorous lesions, and Paget’s disease. AP imaging is useful for patients who cannot be imaged in the PA direction.
Prior confirmation
Considering the increased radiation exposure to the lens, we are considering imaging in the PA direction instead of the AP direction. Confirm the purpose of the examination. Remove any obstacles (hairpins, eyeglasses, earrings, necklaces, dentures, etc.).
Positioning
Prone position (PA) or supine position (AP) (standing or sitting is also acceptable).
Align the mid-sagittal plane with the long axis of the film.
From the head side, ensure that the distance between both external auditory canals and the film is equal.
Place a marker (R or L) without fail.
Retract the chin and make the OML (Orbitomeatal Line) perpendicular to the film.
→ If it’s a PA view, place a pillow under the chest; if it’s an AP view, use a positioning block as a pillow and elevate the head side.
CR, distance, field size
CR : Direct the X-ray beam perpendicular to the intersection of the mid-sagittal plane and the OML (Orbitomeatal Line). If chin retraction is difficult, angle the beam according to the angle of the OML.
Distance : 100cm
Field size : Include the entire head, including the soft tissues.
Exposure condition
75kV / 16mAs
Grid ( + )
Suspend respiration.
Image, check-point
Normal (Radiopaedia)
The suture line is projected symmetrically on both sides, and the distance from the orbital rim to the outer edge of the skull is equal and depicted symmetrically.
Both the outer and inner plates should be observable.
The conical process should be projected in the upper 1/3 of the orbit.
Ensure that the following anatomical structures are observed under appropriate imaging conditions (frontal bone, crista galli, internal auditory canal, frontal sinus, ethmoid sinuses, conical process, and sella turcica).
In AP view, structures such as the orbits appear more magnified compared to PA view.
Videos
AP view 2:39~
PA view 4:40~
Related materials